Moderate RV Dysfunction Is an Indicator of Intermediate Risk1
An early indicator of PAH progression is worsening right heart function.2
With most patients at intermediate risk at diagnosis, their right heart function needs to be assessed every 3 to 6 months. This may identify progression early to help patients achieve low-risk status in a timely manner.1,3
RV Changes Occur Before Other Indicators of PAH Progression2

Recent Guideline Updates Place a Greater Emphasis on RV Function1
- Both REVEAL Lite 2 and the updated 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines emphasize using echocardiography when assessing RV function and its effect on PAH progression1,5
- Right heart imaging results may suggest worsening prognosis, even if risk status is stable5
- A TAPSE of ≤18 mm or moderate/severe tricuspid regurgitation (TR) have been associated with worse outcomes in the intermediate risk PAH population6
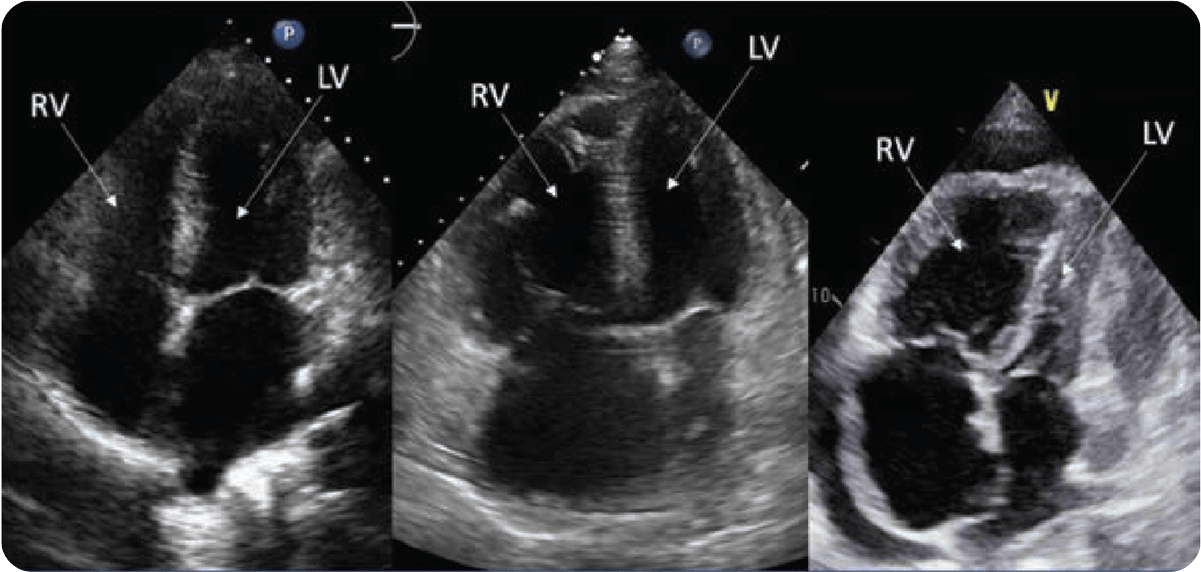
Progressive Worsening
